Publications
Peruzzi, C. D.; Miller, S. L.; Dannatt, J. E.; Ghaffari, B.; Maleczka, R. E., Jr.; Smith, M. R., III Organometallics, 2024, 43, 1208.
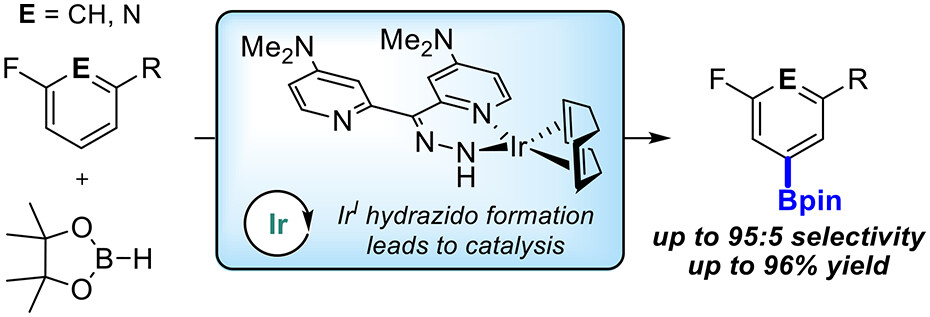
Abstract:
Ir-catalyzed C–H borylations of fluorinated and cyanated arenes with high meta-to-F/CN are described. Use of a dipyridyl hydrazone framework as the ancillary ligand and pinacolborane (HBpin) as the functionalizing reagent generates catalysts that are significantly more active and selective than 4,4′-di-tert-butyl-2,2′-bipyridine (dtbpy) for both electron-deficient and electron-rich substrates. Investigation of the ligand framework resulted in the observation of formal N-borylation of the hydrazone by HBpin, as evidenced by NMR spectroscopy and X-ray crystallography. Subsequent stoichiometric reactions of this adduct with an iridium precatalyst revealed the formation of an unusual IrI hydrazido. Isolation and use of this hydrazido reproduce the selectivity of in situ generated catalysts, suggesting that it leads to formation of the active species.
Draper, M. R.; Waterman, A., IV; Dannatt, J. E.; Patel, P. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2024, 26, 7907.
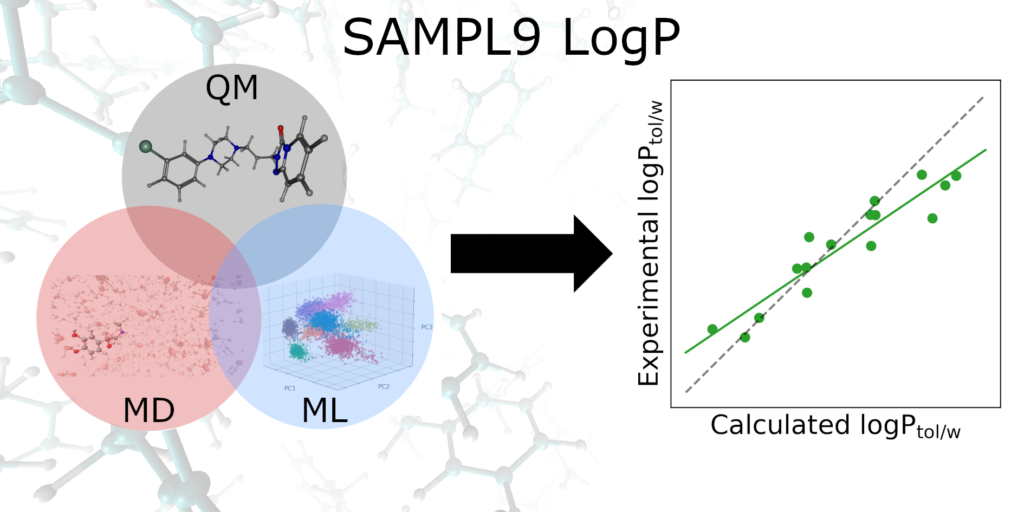
Abstract: The partition coefficient (log P) is an important physicochemical property that provides information regarding a molecule’s pharmacokinetics, toxicity, and bioavailability. Methods to accurately predict the partition coefficient have the potential to accelerate drug design. In an effort to test current methods and explore new computational techniques, the statistical assessment of the modeling of proteins and ligands (SAMPL) has established a blind prediction challenge. The ninth iteration challenge was to predict the toluene–water partition coefficient (log Ptol/w) of sixteen drug molecules. Herein, three approaches are reported broadly under the categories of quantum mechanics (QM), molecular mechanics (MM), and data-driven machine learning (ML). The three blind submissions yield mean unsigned errors (MUE) ranging from 1.53–2.93 log Ptol/w units. The MUEs were reduced to 1.00 log Ptol/w for the QM methods. While MM and ML methods outperformed DFT approaches for challenge molecules with fewer rotational degrees of freedom, they suffered for the larger molecules in this dataset. Overall, DFT functionals paired with a triple-ζ basis set were the simplest and most effective tool to obtain quantitatively accurate partition coefficients.
Dannatt, J. E.; Yadav, A.; Smith, M. R., III; Maleczka, R. E., Jr. Tetrahedron, 2022, 109, 132578.
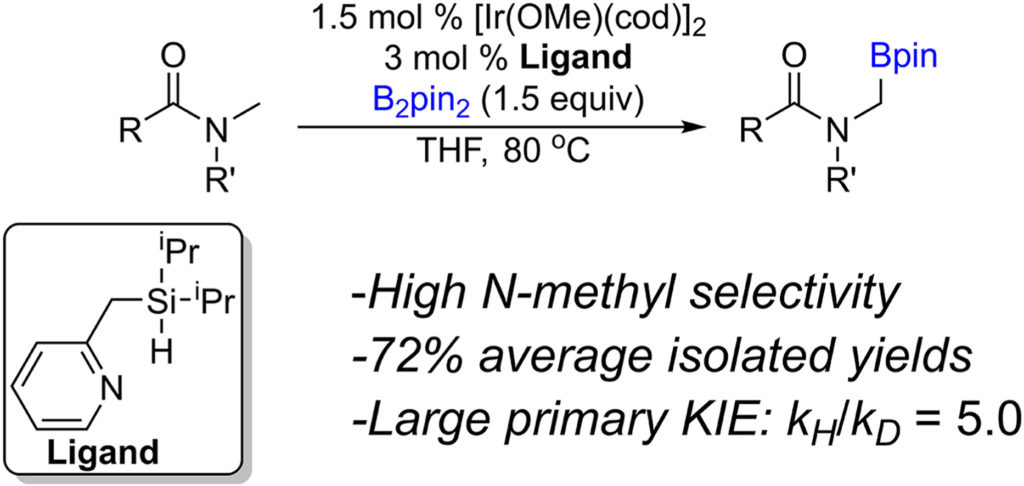
Abstract:
A bidentate monoanionic ligand system was developed to enable iridium catalyzed C(sp3)–H activation borylation of N-methyl amides. Borylated amides were obtained in moderate to good isolated yields, and exclusive mono-borylation allowed the amide to be the limiting reagent. Selectivity for C(sp3)–H activation was demonstrated in the presence of sterically available C(sp3)–H bonds. Competitive kinetic isotope studies revealed a large primary isotope effect, implicating C–H activation as the rate limiting step.
Baker, A. J.; Dannatt, J. E. J. Chem. Ed. 2020, 97, 3235.
Abstract:
This communication contains the experience of two early-career organic professors at primarily undergraduate institutions during the rapid transition to an online learning environment during the COVID-19 pandemic. The techniques and methods for transitioning both the organic lecture and lab of two class sizes (∼50 and ∼10) are juxtaposed, and conclusions are drawn that provide insight into improvements for both online and on-site learning.
Badre-Deen, B.; Dannatt, J. E.; King, A. K.; Lee, A.; Maleczka, R. E., Jr. Commun. 2019, 55, 8623.
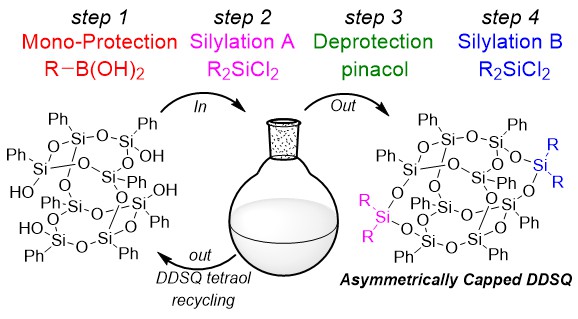
Abstract:
A strategically novel synthesis of nano-sized, asymmetrically functionalized double-decker shaped silsesquioxanes (DDSQ) is reported. Selective protection with a boronic acid affords the crucial mono-protected intermediate en route to the asymmetric products. Generation of symmetric by-products is minimized by judicious choice of base, and high recovery of recyclable starting DDSQ tetraol is achieved.
Vogelsang, D. F.; Dannatt, J. E.; Schoen, B. W.; Maleczka, R. E., Jr.; Lee, A. ACS Applied Nano Materials 2019, 2, 1223.
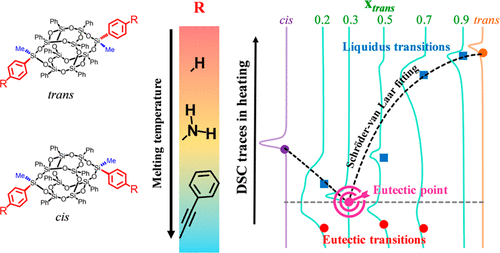
Abstract:
Closed double-decker shaped silsesquioxanes (DDSQ-(Ph)8-2((Me)(R))) with R as phenyl, para-phenylamine, and para-phenylethynyl phenyl were synthesized. Isolation of nearly pure trans and cis isomers was obtained by fractional recrystallization. Crystallographic and thermal characteristics of these isolated isomers were obtained by X-ray diffraction of a single crystal and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). It was observed that melting temperature increases as the size of the R group decreases from para-phenylethynyl phenyl to phenyl and the magnitude of the entropy difference at melting increases as the size of the R group increases. Isolated isomers were then mixed to different cis-to-trans ratios, and their thermal characteristics investigated by DSC. The upper portion of the phase diagram was constructed for these DDSQ compounds using results from DSC traces. Interestingly, cis and trans isomers of these DDSQ compounds form a binary eutectic. Experimentally observed eutectic composition and temperature were found to be close to the calculated values based on the ideal eutectic mixing rule. These data allow users to broaden the thermal processability window by reducing the system melting temperature without affecting the reaction onset temperature of the functional groups.
Vogelsang, D. F.; Dannatt, J. E.; Maleczka, R. E., Jr.; Lee, A. Polyhedron 2018, 115, 189.
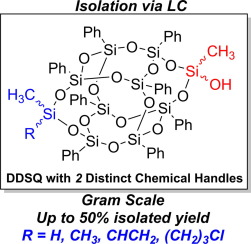
Abstract:
A synthetic path to asymmetric side-capped double-decker shaped silsesquioxanes (DDSQ) and subsequent isolation is described. By strategically using a combination of dichloro and trichlorosilane capping agents, a resultant product with mixed silanol functionalities was obtained. The use of preparatory liquid chromatography (LC) cleanly separated DDSQ compound with asymmetric functionality, and HPLC provided a quantitative technique to analyze mixture ratios. These mixture ratios did not follow the expected statistical trend due to the steric effects on the rate of capping. As a consequence, a decreased amount of the desired asymmetric DDSQ was observed in some cases. This was overcome by varying the ratio of capping agents. Overall, this work demonstrates access to asymmetric DDSQ cages is feasible, and LC is an effective separation technique.
Smith, M. R., III; Bisht, R.; Haldar, C.; Pandey, G.; Dannatt, J. E.; Ghaffari, B.; Maleczka, R. E., Jr.; Chattopadhyay, B. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 6216.
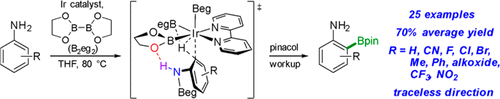
Abstract:
High ortho selectivity for Ir-catalyzed C–H borylations (CHBs) of anilines results when B2eg2 (eg = ethylene glycolate) is used as the borylating reagent in lieu of B2pin2, which is known to give isomeric mixtures with anilines lacking a blocking group at the 4-position. With this modification, high selectivities and good yields are now possible for various anilines, including those with groups at the 2- and 3-positions. Experiments indicate that ArylN(H)Beg species are generated prior to CHB and support the improved ortho selectivity relative to B2pin2 reactions arising from smaller Beg ligands on the Ir catalyst. The lowest-energy transition states (TSs) from density functional theory computational analyses have N–H···O hydrogen-bonding interactions between PhN(H)Beg and O atoms in Beg ligands. Ir-catalyzed CHB of PhN(H)Me with B2eg2 is also highly ortho-selective. 1H NMR experiments show that N-borylation fully generates PhN(Me)Beg prior to CHB. The TS with the lowest Gibbs energy was the ortho TS, in which the Beg unit is oriented anti to the bipyridine ligand.
Chattopadhyay, B.; Dannatt, J. E.; Andujar-De Sanctis, I. L.; Gore, K. A.; Maleczka, R. E., Jr. Singleton, D. A.; Smith, M. R., III J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 7864. (Highlighted in Synfacts 2017, 13, 862.)
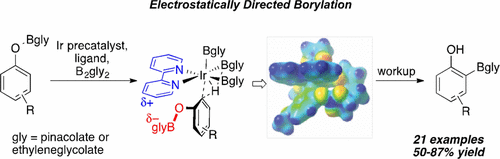
Abstract:
A strategy for affecting ortho versus meta/para selectivity in Ir-catalyzed C–H borylations (CHBs) of phenols is described. From selectivity observations with ArylOBpin (pin = pinacolate), it is hypothesized that an electrostatic interaction between the partial negatively charged OBpin group and the partial positively charged bipyridine ligand of the catalyst favors ortho selectivity. Experimental and computational studies designed to test this hypothesis support it. From further computational work a second generation, in silico designed catalyst emerged, where replacing Bpin with Beg (eg = ethylene glycolate) was predicted to significantly improve ortho selectivity. Experimentally, reactions employing B2eg2 gave ortho selectivities > 99%. Adding triethylamine significantly improved conversions. This ligand–substrate electrostatic interaction provides a unique control element for selective C–H functionalization.
Wolf, C.; Cook, A; Dannatt, J. E. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 2014, 25, 163.
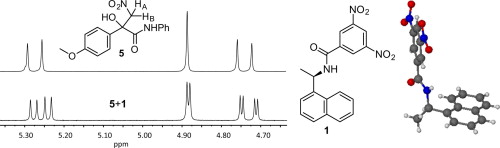
Abstract:
A Whelk-O type chiral solvating agent (CSA) allows NMR enantioresolution of multifunctional tertiary alcohols. Crystallographic analysis of the CSA revealed two conformers, which can be expected to coexist in solution. One conformation affords a chiral cleft that can engage a single enantiomer in simultaneous hydrogen bonding, π–π stacking, and CH/π interactions. This chiral recognition process yields nonequivalent NMR signals for the enantiomers of eighteen substrates even when substoichiometric amounts of the CSA are used.
